In the intricate realm of veterinary science, melanoma, a formidable type of skin cancer, emerges as a significant concern for our cherished canine companions. In this exploration, we delve deeply into the intricate details of melanoma in dogs, shedding light on its characteristics, origins, symptoms, diagnosis, and available treatments. This wealth of knowledge empowers pet owners with indispensable insights, enabling them to provide proactive and attentive care to their beloved furry companions.
1. Decoding Canine Melanoma:
Canine melanoma, a malignant cancer, originates in the pigment-producing cells of a dog’s skin and mucous membranes. These cells, scientifically termed melanocytes, govern the skin, hair, and eye coloration. Melanomas often manifest as dark, irregular lumps or lesions on a dog’s skin, gums, lips, or toenails, signaling the presence of this formidable adversary.

Read more.. Going with Pets: Tips for a Pet-Accommodating Excursion
2. Unraveling Causes and Risk Factors:
While the precise triggers of melanoma in dogs remain elusive, certain factors heighten a dog’s vulnerability. Breeds characterized by darker pigmentation, including Schnauzers, Scottish Terriers, and Doberman Pinschers, are predisposed to this condition. Additionally, although not definitively established, exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation is suspected to contribute, necessitating sun protection for dogs, especially those at elevated risk.
3. Recognizing Symptoms:
Early detection of melanoma is pivotal for effective intervention. Symptoms vary based on the tumor’s size and location. Common indicators include non-healing lumps or sores, alterations in the shape or color of existing moles or skin lesions, swelling, bleeding, and difficulties in eating or swallowing, particularly if the tumor affects the oral cavity or throat.
Read more.. Discovering the Best Accessories for Your Beloved Cats Online
4. Diagnosis and Treatment Strategies:
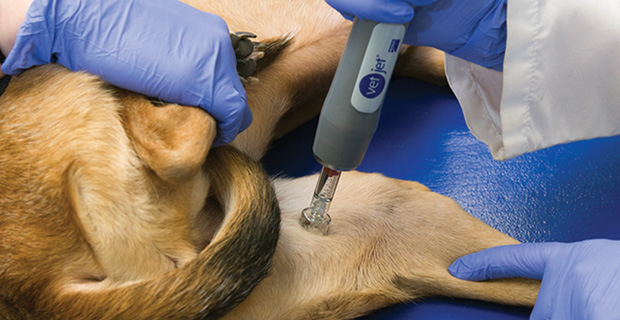
Diagnosing canine melanoma mandates meticulous physical examination, often followed by a biopsy for confirmation. Imaging techniques like X-rays or ultrasounds gauge the disease’s extent. Treatment avenues encompass surgical removal, radiation therapy, immunotherapy, and, in certain cases, chemotherapy. The choice of therapy hinges on factors such as tumor location, size, and stage.
5. Proactive Canine Care:
Mitigating melanoma risks in dogs necessitates reducing UV exposure, particularly for susceptible breeds. This involves creating shaded areas, employing dog-friendly sunscreens, and scheduling walks outside peak sunlight hours. Routine veterinary examinations, encompassing skin evaluations, play a pivotal role in early detection.
Conclusion:
Comprehending melanoma in dogs emerges as a cornerstone for pet owners, fostering an environment of informed and attentive care for their cherished companions. Early identification, swift veterinary attention, and proactive sun protection measures are instrumental in preserving the well-being of dogs prone to this condition. In the pursuit of knowledge and vigilance, pet owners embark on a profound commitment, ensuring a life marked by quality, care, and boundless love for their cherished canine family members.
Read more.. Navigating the Maze: Unveiling the 5 Worst Health Insurance Companies in India